The BC546 and BC547 transistors are both NPN bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) commonly used in low-power amplification and switching circuits. While they are quite similar, there are some differences between the BC546 and BC547. Here's an overview:
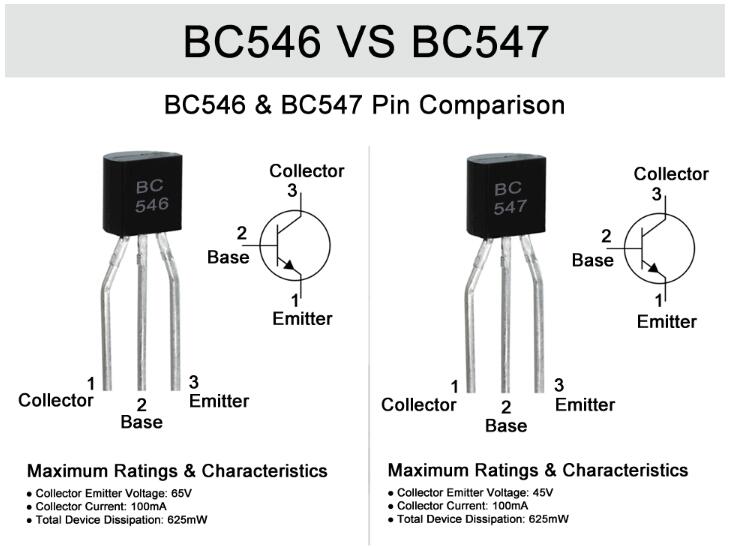
BC546: The BC546 is an NPN transistor with the following characteristics:
-
Maximum Collector Current (IC): The BC546 has a maximum collector current rating of 100 mA (milliamperes), which defines the maximum current allowed to flow through the transistor's collector terminal without causing damage.
-
Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The BC546 typically has a maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 65 volts, indicating the maximum voltage allowed across the collector-emitter junction to avoid potential transistor failure.
-
Current Gain (hFE or β): The current gain of the BC546 transistor typically ranges from 110 to 800. This parameter represents the amplification capability of the transistor and indicates the ratio of the collector current (IC) to the base current (IB).
BC547: The BC547 is also an NPN transistor frequently used in low-power applications. Here are its characteristics:
-
Maximum Collector Current (IC): The BC547 has the same maximum collector current rating as the BC546, which is 100 mA, indicating that both transistors can handle the same maximum current levels.
-
Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The BC547 typically has a maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 45 volts, which is slightly lower than the BC546's 65 volts. This means that the BC547 is designed to operate within lower voltage ranges.
-
Current Gain (hFE or β): The current gain of the BC547 transistor generally ranges from 110 to 800, similar to the BC546.
Ratings & Characteristics Comparison:
| Ratings & Characteristics | BC546 | BC547 |
|---|---|---|
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo) | 65V | 45V |
| Collector Current (Ic) | 100mA | 100mA |
| Total Device Dissipation (PD) | 625mW | 625mW |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 110 To 800 | 110 To 800 |
| Frequency (fT) | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
Differences:
-
Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage: One significant difference between the BC546 and BC547 is the maximum collector-emitter voltage rating. The BC546 can withstand higher voltage levels (up to 65 volts) compared to the BC547, which is limited to 45 volts.
-
Voltage Compatibility: Due to the higher maximum collector-emitter voltage rating, the BC546 may be more suitable for applications that require handling higher voltage levels than what the BC547 can handle.
Similarities:
-
Maximum Collector Current and Current Gain: Both the BC546 and BC547 share the same maximum collector current rating of 100 mA, which means they can handle the same maximum current levels. Additionally, they have similar ranges for current gain (hFE or β), falling between 110 and 800.
-
NPN Transistor Type: Both the BC546 and BC547 transistors are NPN transistors with similar pin configurations and functionality. They are designed as NPN BJTs and have three layers with a negatively-doped layer sandwiched between two positively-doped layers.
It's essential to consider these differences and similarities when selecting a transistor for a particular application. Ensure that the chosen transistor meets the voltage, current, and amplification requirements of the circuit. Refer to the datasheets provided by the manufacturer for detailed specifications and information to ensure proper transistor selection.



